Machine Learning or Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Robotic Process Automation or RPA, both the terms are buzzwords today. AI techniques surround us without even realizing their presence. Automation is revolutionizing business operations for organizations in almost every sector.
The world RPA business size was valued at USD 846 million in 2018 and became the speed-growing part of the worldwide enterprise software market. Also, it is anticipated to register a CAGR of 31.1% in the next five years.
The world artificial intelligence business size was valued at USD 24.9 million in 2018, and it is anticipated to reach a CAGR of 46.2% from 2019 to 2025.
When you look for the trending technologies for 2020, you will find RPA and Artificial Intelligence on the top ten of the list. The trend of machine learning and bots is only going to escalate, which implies that RPA and ML are going to become an invaluable skill to have, and people who take a Machine Learning online course will be in demand.
When you read the above discussion, you find that RPA and AI or ML are quite similar terms and may be interrelated. It is thought that every aspect of automation is related to artificial intelligence. But this is not so. RPA and ML are horizontal techniques, both with different goals and interfaces.
Yes! You are thinking it right. Let’s dive deep into the two terms.
Table of Contents
1. What is RPA or Robotic Process Automation?
Robotic Process Automation is an application of technology that is aimed at the automation of business processes, which is governed by business logic and structured inputs.
That means RPA tools can be used to configure software or a robot for manipulation of data, triggering responses, capture and translate applications for processing transactions, and communicating with other digital systems.
Put, mimicking human actions to perform a series of steps that lead to meaningful activity and doesn’t require human intervention is referred to as robotic process automation.
Application of RPA can be made for basic tasks like replying to an email as well as for very complex tasks like deployment of thousands of bots, each meant to automate jobs in an ERP system.
Today RPA is being used in almost every sector that includes supply chain management, human resources, customer service, healthcare, financial services, accounting, and more.
RPA benefits include the accuracy and consistency of the tasks. It reduces manual labor, and the best part is that it requires no or minimal coding. It increases the productivity of a company and reduces costs by eliminating human intervention.
2. What is Machine Learning?
As per the definition given by Arthur Samuel, a pioneer in the field of Artificial Intelligence and the one who coined the term Machine Learning, ‘Machine Learning is a range of study that proffers computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed.
Machine learning (ML) is a sub-part of Artificial Intelligence (AI). The two terms can be generally used interchangeably.
Machine learning involves improving the learning process of computers based on their experiences, without any human assistance or without being programmed.
First of all, sound quality or relevant data is fed into the system. Then the computer is trained with the help of machine learning models that are based on the data provided and different algorithms.
The type of data and the task to be done form the basis of selecting an algorithm to train the machine or automate the required task.
Let us see the most common example of machine learning.
When you look for some watches online, below comes a recommendation, ‘you may also like,’ and there are pictures of some more eyes that are similar to the one you were looking at.
This standard application of Machine Learning is called ‘Recommendation Engine.’
Another example of Machine Learning is Google, Alexa, and Siri.
Yourself can request them to tell you of your tasks and anything on a smartphone.
It is based on the learning pattern of humans. We see, and we learn from our experiences. Likewise, machines are fed with inputs and related algorithms.
3. Machine Learning vs RPA
When you read the basic introduction of machine learning and RPA, you find them similar; both are involved in the automation of tasks. But if you fall more bass, you find that there are differences in their working and execution.
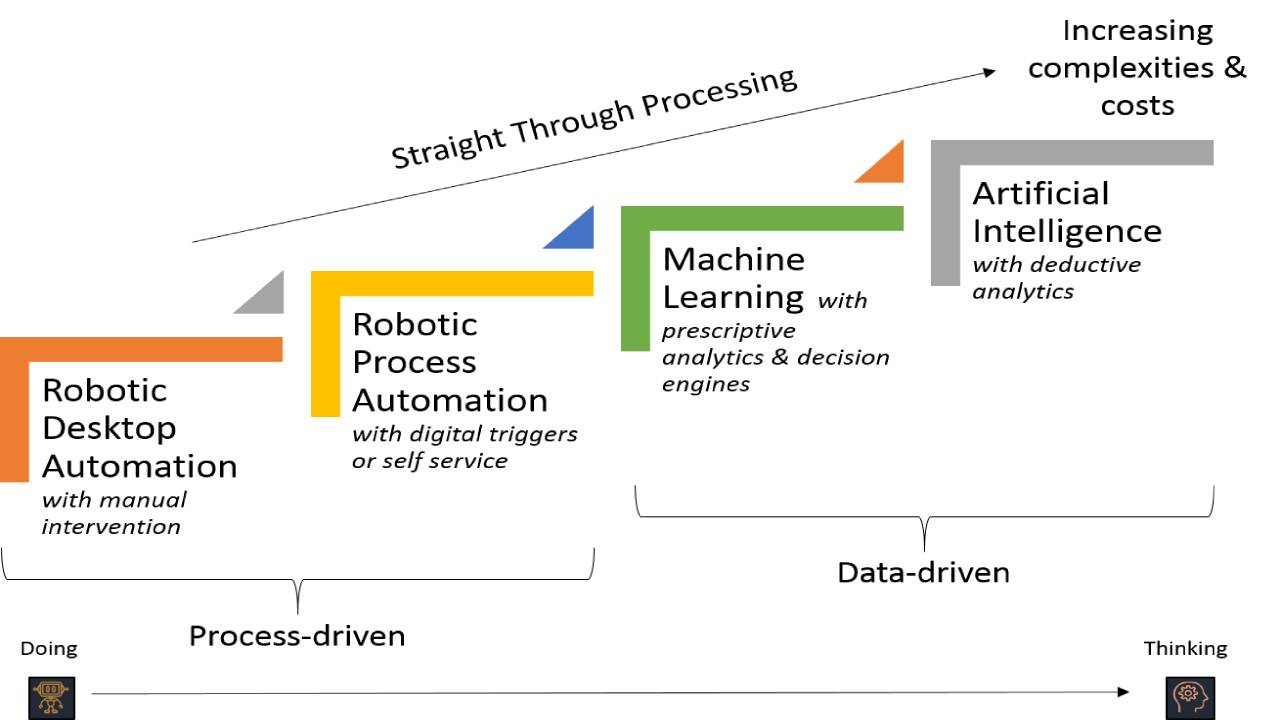
The fundamental difference between RPA and ML is based on Doing and Thinking. While RPA is associated with ‘doing,’ ML is related to ‘thinking’ and ‘learning’ and acts accordingly.
RPA is used for automating repetitive tasks like sending emails or downloading the attachments, retrieving the subject.
On the other hand, ML can manage your mails, pick out useful insights from them, and can also convert unstructured data to structured data for your ease.
The image below shows you how ML and RPA are different.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a software robot that can mimic human actions, whereas ML expresses its artificial intelligence by exhibiting ‘adaptation,’ which is one of its biggest characteristics.
Put, RPA acts more like an essential resource that executes actions based on its configuration and can’t think out of the box.
On the other hand, Machine Learning autonomously improves its performance as the system is fed with observational data and real-time problems, just like humans improve their actions with experience.
The two technologies are also compared by some people as brains over brawn, with RPA being the latter and ML being the former.
Another difference between ML and RPA rests on their area of focus.
RPA, as the term itself implies, is highly process-driven. It is all about automating iterative tasks that are rule-based and typically require communication with multiple and disparate IT systems.
For implementing RPA, the major prerequisite is the process discovery workshop to map the existing process.
On the other hand, ML is data-centric. It is fed with high-quality data and machine learning algorithms. There are no repetitive tasks, but it works on the given input and acts as it has been learned to do so. For example, you can ask your smartphone to set the alarm for you. Then you can ask it to type a message and send it to some recipient. So there is no repetition.
In short, ML is data-centric, and RPA is process-centric.
4. Bottom Line
We now know that RPA and ML, both the technologies are trending these days, both have their different use cases. They have their implications and are applied in almost every sector. Also, both have their benefits too. So you can choose any of them as your career and reach new heights.
RPA and ML are both invaluable solutions that have the potential of enhancing business performance for any organization. They are applied according to the most critical business requirements that can be improved through automation.
Tech India Today
Related posts
Recent Posts
- How Important is Competitor Analysis? November 13, 2023
- Securing the Internet of Things: A Growing Concern October 2, 2023
- When DevSecOps Shines: Reinventing Software Development May 17, 2023
- Implementing Infrastructure As Code (IaC) With DevOps April 21, 2023
- What Can You Gain By Choosing a Reputable HVAC Software Solution? March 19, 2023
Categories
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) (18)
- Augmented Reality (AR) (5)
- Automotive (7)
- Blockchain (2)
- Business (45)
- Career (4)
- Cloud Computing (6)
- Computers (4)
- Content Management System (1)
- Cryptocurrency (1)
- Cybersecurity (7)
- Data Science (1)
- Digital Marketing (32)
- E-commerce (1)
- Education (6)
- Electronics & Hardware (10)
- Entertainment (5)
- Finance (9)
- Gadgets (23)
- Games (3)
- HTTP (3)
- Industry (2)
- Infographics (3)
- Internet (138)
- Internet of Things (IoT) (22)
- Job (3)
- Lifestyle (2)
- Machine Learning (7)
- Marketing (45)
- Marketplace (2)
- Mobile Apps (20)
- Natural Language Processing (2)
- Network (15)
- News & Trends (15)
- Operating System (OS) (6)
- Programming (10)
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) (13)
- Security (19)
- SEO (24)
- Social Media (29)
- Software (35)
- Tech India Today (1)
- Technology (166)
- Virtual Reality (VR) (2)
- Web Apps (12)
- WordPress (1)
- Workflow (2)
- Workforce (2)
- Workplace (1)
- Workspace (1)